Teaching
Below is a comprehensive list detailing the classes for which I served as an undergraduate teaching assistant at UCSD. Instructors are listed in the order in which I worked with them. Where available, instructor evaluations are attached.
My responsibilities:
- Automated the grading process by developing test cases and grading systems in Python, Java, and Stata. Deployed the autograder using Docker on AWS EC2 instances, specifically through Gradescope.
- Assisted over 3,000 students by conducting regular technical office hours, creating and grading assignments and exams, and overseeing the class forum and logistics.
- Guided and mentored new staff, equipping them with the managerial and technical skills required to excel as course assistants.
Cognitive Science

|
Neural Networks and Deep LearningProf. Zhuowen Tu UCSD COGS 181 WI24 website This course will cover the basics about neural networks, as well as recent developments in deep learning including deep belief nets, convolutional neural networks, recurrent neural networks, long-short term memory, and reinforcement learning. We will study details of the deep learning architectures with a focus on learning end-to-end models for these tasks, particularly image classification. |
Computer Science and Engineering
|
Introduction to Machine LearningProf. Edwin Solares UCSD CSE 151A WI24 Broad introduction to machine learning. The topics include some topics in supervised learning, such as k-nearest neighbor classifiers, decision trees, boosting, and perceptrons; and topics in unsupervised learning, such as k-means and hierarchical clustering. In addition to the actual algorithms, the course focuses on the principles behind the algorithms. |
|
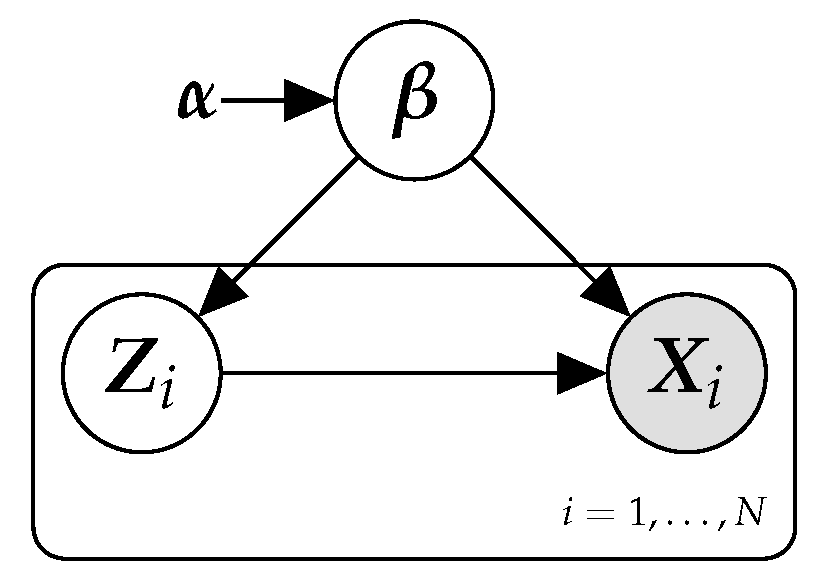
AI: Probabilistic ModelsProf. Mary Anne Smart UCSD CSE 150A S123 evaluation / website Introduction to probabilistic models at the heart of modern artificial intelligence. Specific topics to be covered include probabilistic methods for reasoning and decision-making under uncertainty; inference and learning in Bayesian networks; prediction and planning in Markov decision processes; applications to intelligent systems, speech and natural language processing, information retrieval, and robotics. |
Data Science

|
The Practice and Application of Data Science (X3)Prof. Tauhidur Rahman, Prof. Suraj Rampure UCSD DSC 80 WI24, SP23, WI23 evaluation / website Students master the data science life-cycle and learn many of the fundamental principles and techniques of data science spanning algorithms, statistics, machine learning, visualization, and data systems. |
|
Theoretical Foundations of Data Science IIProf. Yusu Wang UCSD DSC 40B SP23 evaluation / website DSC 40B, the second course in the sequence, introduces fundamental topics in combinatorics, graph theory, probability, and continuous and discrete algorithms with applications to data analysis. |
|
Theoretical Foundations of Data Science IProf. Truong Son Hy and Prof. Mahdi Soleymani UCSD DSC 40A FA22 evaluation / website DSC 40A will introduce fundamental topics in machine learning, statistics, and linear algebra with applications to data analysis. |

|
Data Structures and Algorithms for Data ScienceProf. Soohyun Liao and Prof. Marina Langlois UCSD DSC 30 SP22 website Programming techniques including encapsulation, abstract data types, interfaces, algorithms and complexity, and data structures such as stacks, queues, priority queues, heaps, linked lists, binary trees, binary search trees, and hash tables with Java. |

|
Programming and Basic Data Structures for Data Science (x4)Prof. Marina Langlois UCSD DSC 20 WI24, SP22, WI22, FA21 website Programming techniques including recursion, higher-order functions, function composition, object-oriented programming, interpreters, classes, and simple data structures such as arrays, lists, and linked lists. |

|
Principles of Data ScienceProf. Suraj Rampure and Prof. Janine Tiefenbruck and Prof. Rod Albuyeh UCSD DSC 10 FA23 website This first course in data science introduces students to data exploration, statistical inference, and prediction. It introduces the Python programming language as a tool for tabular data manipulation, visualization, and simulation. Through homework assignments and projects, students are given an opportunity to develop their analytical skills while working with real-world datasets from a variety of domains. |
Economics

|
Econometrics (X2)Prof. Gordon Dahl, Prof. Maria Candido UCSD ECON 120B WI23, FA22 evaluation / website This course prepares students for empirical analysis in an academic or business setting. It covers the fundamentals of regression, including estimation and hypothesis testing in a univariate and multivariate framework. It presents ideas using the “potential outcomes” framework and makes the important distinction between prediction and causality. The course discusses reasons why estimators may be biased or inconsistent, and how both randomized experiments and natural experiments can be used to obtain causal estimates. |
Mathematics
|
Mathematical ReasoningProf. John Eggers UCSD MATH 109 SP22* evaluation / website This course uses a variety of topics in mathematics to introduce the students to rigorous mathematical proof, emphasizing quantifiers, induction, negation, proof by contradiction, naive set theory, equivalence relations and epsilon-delta proofs. |

|
Introduction to Differential Equations (X2)Prof. Nandagopal Ramachandran, Prof. Ming Xiao UCSD MATH 20D FA22*, SP21* evaluation / website Ordinary differential equations: exact, separable, and linear; constant coefficients, undetermined coefficients, variations of parameters. Systems. Series solutions. Laplace transforms. Techniques for engineering sciences. Computing symbolic and graphical solutions using MATLAB. |
|
Calculus and Analytic Geometry for Science and EngineeringProf. Emmanuel Vavalis UCSD MATH 20C WI21* website Vector geometry, vector functions and their derivatives. Partial differentiation. Maxima and minima. Double integration. |
|
Calculus for Science and Engineering (X2)Prof. Yucheng Tu, Prof. Yuming Zhang and Prof. Jacob Sterbenz UCSD MATH 20A WI22, FA21 evaluation / website Foundations of differential and integral calculus of one variable. Functions, graphs, continuity, limits, derivative, tangent line. Applications with algebraic, exponential, logarithmic, and trigonometric functions. Introduction to the integral. |

Leave a comment